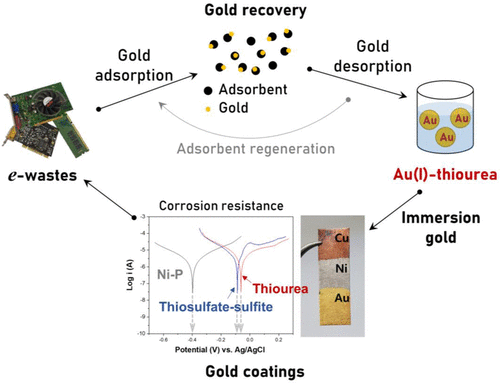
Gold electroless plating for surface finishing of electronic circuits, named electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG), is widely practiced in the electronics packaging industry. Noncyanide substitutions of the current cyanide bath for immersion gold are being sought for environmental and safety reasons. Herein, as a promising option, a bath using a noncyanide gold complex, Au(I)–thiourea, was developed. The kinetics of gold deposition were estimated with respect to gold concentration, thiourea concentration, pH, and temperature; the transfer coefficient of gold concentration and activation energy were found to be 0.697 and 36.69 kJ·mol–1, respectively. In addition, the quality of gold coating in terms of corrosion resistance was verified by electrochemical analysis. The relationship between particle size and corrosion resistance of the coating was confirmed by morphology observation through scanning electron microscopy and Tafel plots. The corrosion potential of the gold layer with thiourea was found to be −62 mV, close to that of the layer using a thiosulfate–sulfite bath, with an advantage of faster deposition rate. The results suggest Au(I)–thiourea can serve as an eco-friendly and field-implementable option for the ENIG process, helping to realize a closed-loop process of gold: recovering the precious metal from electronic wastes and reusing it in new products.