Chapter 2 in Engineered Nanoparticles and the Environment: Biophysicochemical Processes and Toxicity, Edited by B. Xing, C. D. Vecitis, N. Senesi.
WILEY-IUPAC Series in Biophysico-Chemical Processes in Environmental Systems
Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
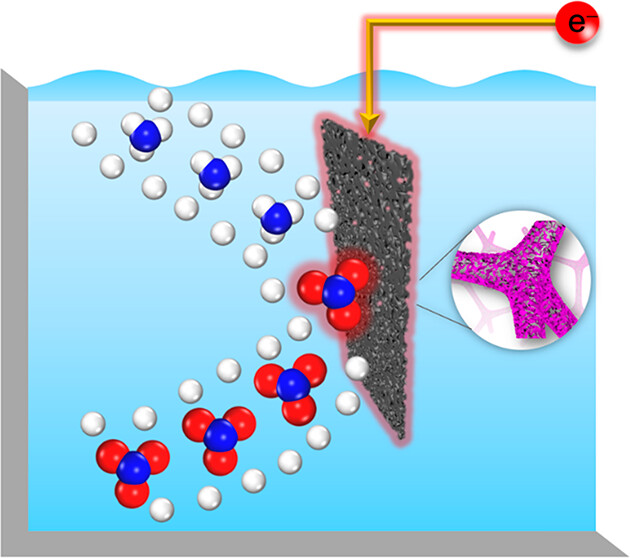
In this chapter, water treatment processes using nanoparticles and studies related to the removal of waterborne contaminants, such as anionic, cationic, and organic pollutants, will be reviewed.